| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- 이펙티브자바
- 알고리즘
- Database
- select
- db
- Effective Java
- Spring
- mybatis
- 그리디알고리즘
- 백준
- join
- springboot
- Greedy
- 데이터베이스
- 탐욕법
- 코테
- java
- 피보나치
- IntelliJ
- mariaDB
- 정렬
- DP
- 우선순위큐
- 프로그래머스
- 깊이우선탐색
- DFS
- 다이나믹프로그래밍
- BFS
- 너비우선탐색
- SQL
Archives
- Today
- Total
땀두 블로그
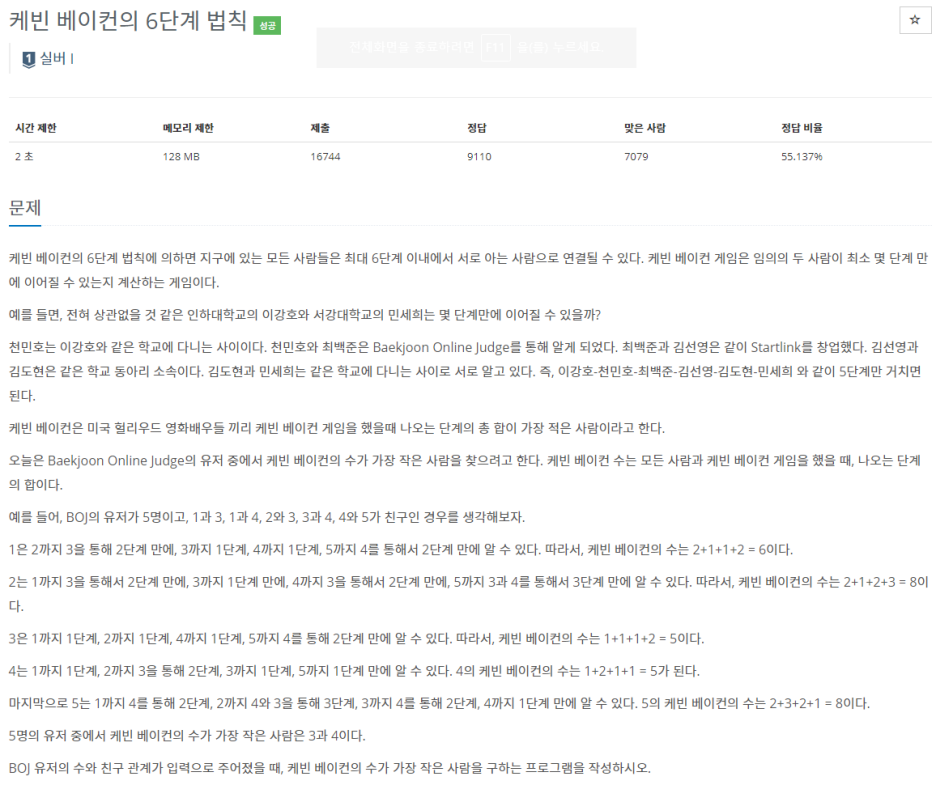
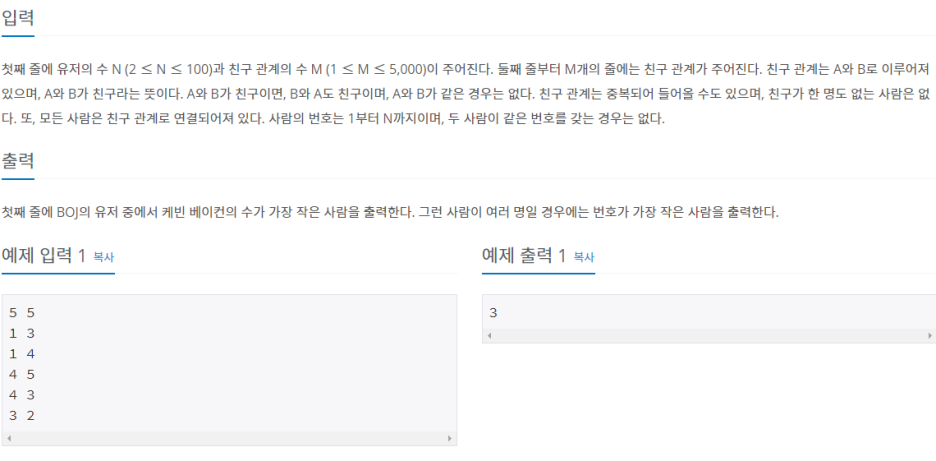
[백준] 1389번 - 케빈 베이컨의 6단계 법칙 본문
BFS로 해결할 수 있는 문제이다. 이 문제에서는 N명의 사람만큼 연산을 수행하고 N-1명에게 도달하는 합을 구하느라 자잘한 배열들과 인덱스 값 저장할 것들을 많이 사용하였는데 아이디어만 떠오르면 간단히 해결할 수 있는 문제였다. 문제에서 각각의 시작점 노드가 필요하므로 visited배열을 반복문이 수행될 때 마다 새로 만들어주어서 사용하였다.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class p1389 {
public static int a;
public static int b;
public static int[][] rst;
public static int[][] ary;
public static boolean[] visited;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
a = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
b = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
ary = new int[a + 1][a + 1];
rst = new int[a + 1][a + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int x = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int y = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
ary[x][y] = 1;
ary[y][x] = 1;
}
int idx = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= a; i++) {
visited = new boolean[a + 1];
bfs(i);
}
int[] sum = new int[a + 1];
sum[0] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 1; i <= a; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= a; j++) {
sum[i] += rst[i][j];
}
if (sum[0] > sum[i]) {
sum[0] = sum[i];
idx = i;
}
}
System.out.println(idx);
}
public static void bfs(int start) {
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer>();
q.add(start);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int n = q.poll();
for (int i = 1; i <= a; i++) {
if (visited[i] == false && ary[n][i] == 1) {
q.add(i);
rst[start][i] += rst[start][n] + 1;
visited[i] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
'알고리즘 > 백준' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준] 1120번 - 문자열 (0) | 2022.03.22 |
|---|---|
| [백준] 2667번 - 단지번호 붙이기 (0) | 2022.03.22 |
| [백준] 11022번 - A+B-8 (0) | 2022.03.22 |
| [백준] 11021번 - A+B-7 (0) | 2022.03.22 |
| [백준] 15552번 - 빠른 A+B (0) | 2022.03.22 |
Comments




